What s the least obese country
Obesity Rates by Country 2024
When a person's weight is higher than what is considered healthy for their height, their condition is described as overweight or obese. Bodyweight results from several factors, such as poor nutritional choices, overeating, genetics, culture, and metabolism. Obesity is linked to many health complications and diseases, such as diabetes, heart disease, certain types of cancer, and stroke. Additionally, obesity is the leading preventable cause of preventable death. Despite the negative effects these conditions can have on one's health, more people are overweight or obese today than ever before in history. In fact, obesity is considered a modern epidemic in most parts of the world. Worldwide obesity has nearly tripled since 1975, with about 13% of adults being obese and about 39% of adults being overweight.
BMI explained
The most commonly used method of measuring obesity is the Body Mass Index, or BMI, which divides a person's weight (in kilograms) by their height (in meters) squared. Medically speaking, BMI scores break down as follows:
- BMI under 18.5 = underweight
- BMI 18.5 to <25 = healthy
- BMI 25 to <30 = overweight
- BMI 30 to <35 = obese (class 1)
- BMI 35 to <40 = obese (class 2)
- BMI 40 or higher = obese (class 3 - morbid)
BMI is not a perfect measure. In particular, it can sometimes give a "false positive" score to athletic individuals, whose high BMIs are due not to excess body fat, but to excess muscle. For example, extremely fit NFL quarterback Russell Wilson measured 5'11" tall and 215 pounds in 2016, which gave him a BMI of 30.0, or obese. NBA superstar and wellness enthusiast Lebron James had a BMI of 27.5 in 2012, which qualified as overweighta clear misdiagnosis. As a result of this inaccuracy, many medical experts are switching to waist-to-height ratio, or WHtR, which compares the circumference of a person's waist to their height. If the waist is more than half the height, (or more than 6/10 the height for those over 50), that person is obese. WHtR is considered much more accurate than BMI, but is also much newer. Over time, as it is adopted by more countries, WHtR could easily replace BMI as the de facto measure of a person's weight health.
Obesity by Country
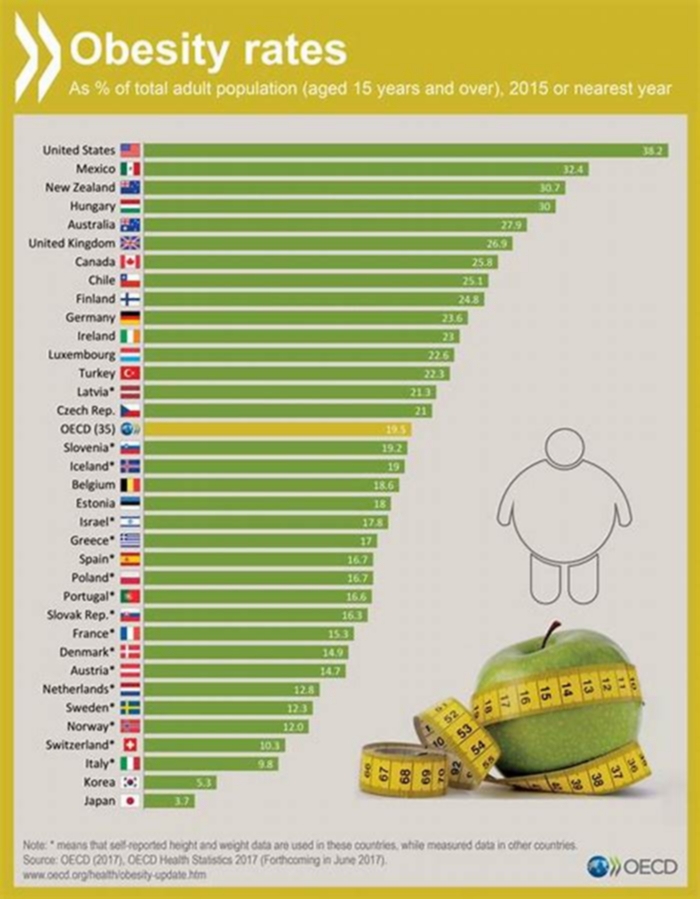
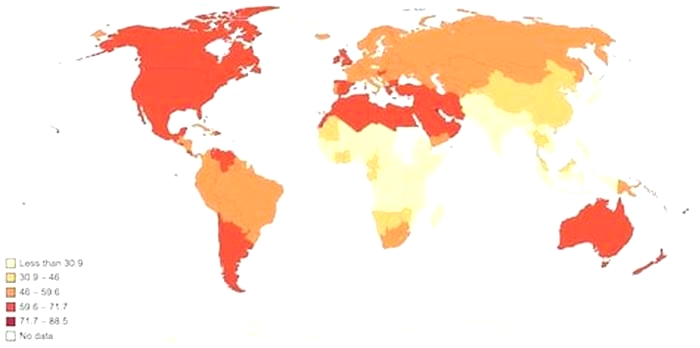
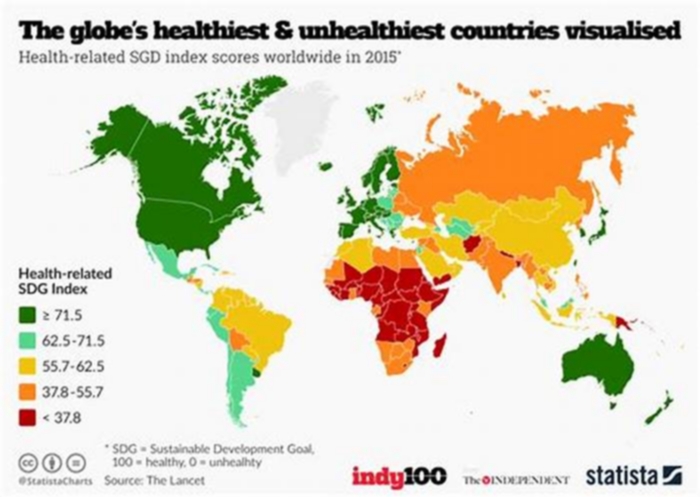
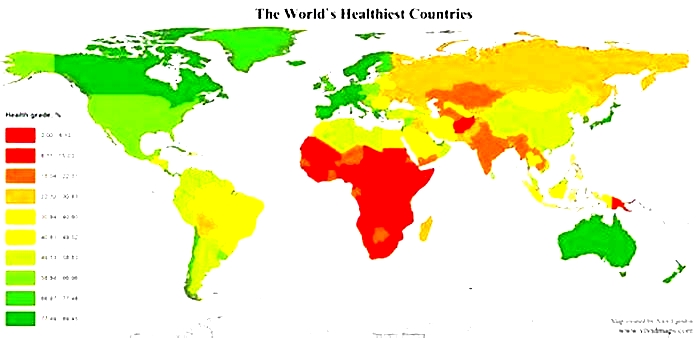
Obesity rates vary significantly by country as a result of different lifestyles and diets. There is no direct correlation between the obesity rate of a country and its economic status; however, wealthier countries tend to have more resources to implement programs, campaigns, and initiatives to raise awareness and education people about what they are consuming. These are among the healthiest countries globally. Some regions of the world, such as the South Pacific, have seen alarming increases in obesity rates within the past five years. Some governments, such as the United States government, have launched campaigns in recent years to promote healthier lifestyles and being active.
The 10 Most Obese Countries in the World
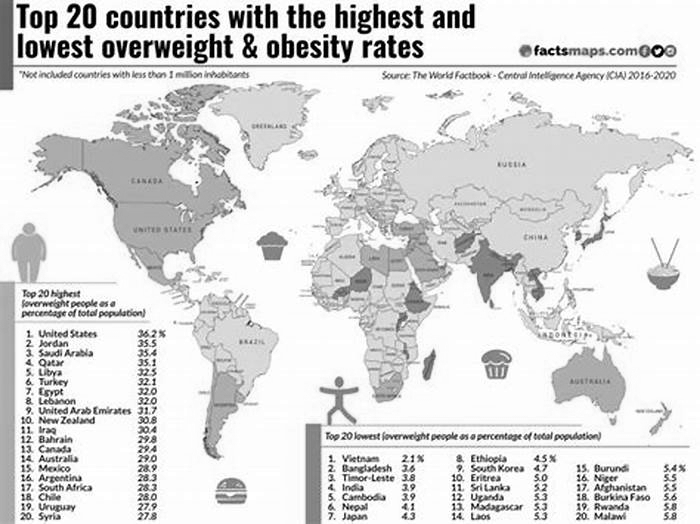
The most obese country by average BMI is the Cook Islands, which has an average BMI of 32.9. Nauru follows with 32.5, then Niue with 32.4. Samoa and Tonga both have average BMIs of 32.2. Finishing the top ten most obese countries are Tuvalu (30.8), Kiribati (30.1), Saint Lucia (30.0), Micornesia (29.7), and Egypt (29.6). What eight of these countries have in common is being located in the South Pacific. When looking at the percentage of obese adults, the list looks a little different. The most obese country by percentage of obese adults is Nauru, with 61% of adults falling in the obese category. Cook Islands fllows with 55.9%, and Palau just under that at 55.3%. Three other countries have adult populations that are over 50% obese: the Marshall Islands (52.9%), Tuvalu (51.6%), and Niue (50%). Finishing the list are Tonga (48.2%), Samoa (47.3%), Kiribati (46.0%), Micronesia (45.8%). The Pacific island nations appear prominently, with Saint Lucia and Egypt serving as the only non-Oceania countries on either list. Type 2-diabetes is a large concern among the people of many of these countries. Multiple theories exist as to why this particular region is so susceptible to obesity, including the growth of unhealthy fast food, the rise of frying as a means of food preparation, and a possible genetic predisposition toward higher BMIs.
The United States has the 12th highest obesity rate in the world at 36.2%. Obesity rates vary significantly between states](/state-rankings/obesity-rate-by-state), ranging from 23% to 38.10%. This is due to the same dietary, environmental, and cultural factors that cause variations between countries. Diet is primarily to blame, with Americans receiving mixed messages about what they should be eating and how much of it. Faced with mouth-watering advertisements served alongside campaigns promoting daily physical activity and proper nutrition, many Americans opt for fast, cheap, and filling options such as processed packaged food, fast food, and larger portions. This often leads to a diet rich in fat, calories, and sodium (the "butter, sugar, salt" trifecta) and low in vitamins and nutrients.
Top 10 Least Obese Countries in the World
When looking at average BMI, three countries tie for the least obese country in the world, with an average BMI of 21.1: Madagascar, Eritrea, and Ethiopia. Five other countries have average BMIs under 22: Timor-Leste (21.3), Burundi (21.6), Japan (21.8), China (21.9) and India (21.9). Bangladesh (22.0) and Burkina Faso (22.1) finish the list. Japan's presence here is perhaps unsurprising given that the national dietwhich emphasizes seafood, freshness, modest portions, and minimal added sugar or dairy fatis a very healthy approach (as evidenced by the fact that Japanese life expectancy is among the highest on Earth). However, many of the other countries on this list struggle with famine and povertywhich is the wrong way to achieve a low BMI.
Countries By Obesity
Like malnutrition and underweight, obesity is a global health problem and one of the leading causes of health complications. The majority of the global population lives in countries where obesity and overweight kill more than malnutrition and underweight. Since 1975, the number of obese globally has almost tripled as per the WHO report. In 2016, over 650 million adults, 18 years or older were obese. In 2019, 38 million children below the age of five were either obese or overweight.
Contents:
What Is Obesity?
Obesity is a medical condition resulting from an accumulation of excess fat in the body. When one takes in more calories than they burn by normal daily activities or exercise, the excess calories accumulate in the body, leading to obesity. However, people are only described as obese if their body mass index (BMI) is over 30. People with a BMI of 25-30 are described as overweight. The excess fat in the body exposes one to serious health problems and diseases, such as high blood pressure, heart diseases, and certain cancers.
Regional Differences In Obesity
Obesity is responsible for close to 5 million deaths annually, or 8% of the global deaths (2017), representing a 3.5% increase from 4.5% in 1990. However, the proportion varies across different continents. In 2017, over 15% of the deaths were attributed to obesity across North Africa, Eastern Europe, Latin America, and Central Asia because of its high prevalence.
Oceania is the worlds most obese region, with 8 of the top ten most obese countries globally located in the region. In the eight Oceania countries, obesity is so prevalent that more than 45% of the population is above the red line. The high rate of obesity in the region is attributed to a sedentary lifestyle and cultural factors, such as lack of proper public education on health and diet.
Most of the least obese countries are located in South Asia, East Asia, Southeast Asia, and Sub-Saharan Africa regions. In most of these countries, less than 10% of the adults are obese. The obesity rate is particularly lower in low and middle-income countries where malnutrition and access to food remain a major challenge. However, in some high-income countries like Singapore and South Korea, specific policy interventions are bearing fruits. For instance, South Korea allocates a budget to support obesity programs and nutritional management in schools.
10 Most Obese Countries
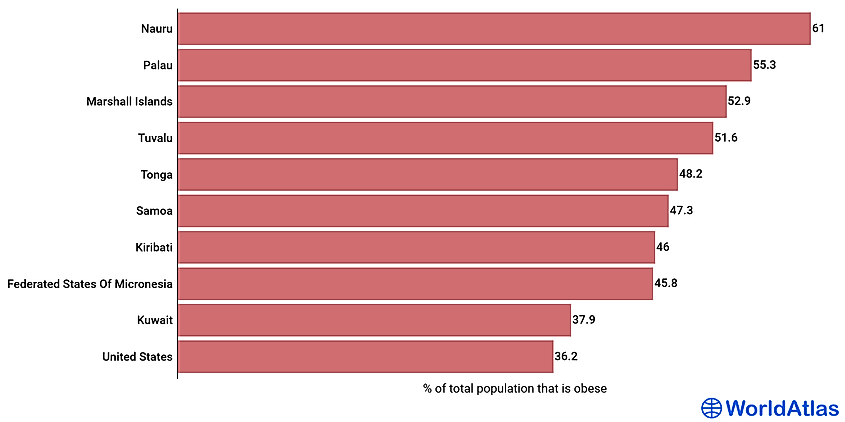
Nauru, an island country in the Oceania region, is the worlds most obese country, with 61% of the adult population suffering from obesity. The country has an average BMI of 34-35. Additionally, up to 83% of Nauruan are overweight. Importation of large quantities of Western foods, lack of physical exercise, cultural preference for overweight and obesity, and lack of proper health education are some of contributing factors to the countrys high obesity rate.
55.3% of Palaus adult population are obese, making Palau the worlds second-most obese country. The countrys obesity prevalence is higher for both men and women than the regional average. 58.8% and 51.8% of adult women and men respectively are obese. A sedentary lifestyle and inadequate health education and diet are the main contributing factors to Palau's high obesity rate.
Marshall Islands, Tuvalu, and Tonga complete the list of the five most obese countries. In the Marshall Islands, 52.9% of the adult population are obese, while in Tuvalu and Tonga, the proportion of the obese is 51.6% and 48.2% respectively. The diets of these three island countries comprise mainly imported processed food rich in high sugar. Besides, most of these Island countries do not provide proper education on health and diet, nor highlight the need for physical exercise. The other three Oceania countries with a high proportion of the obese population are Samoa (47.3%), Kiribati (46%), and the Federal State of Micronesia (45.8%).
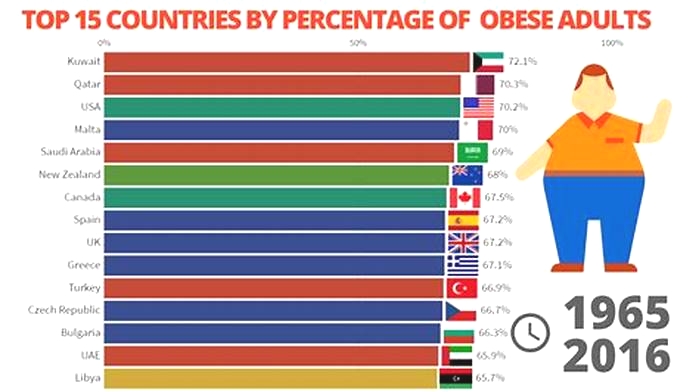
Kuwait is Asias fattest country and the worlds 9th most obese country, with 37.9% of its population suffering from obesity. The risk of obesity in the country results from a sedentary lifestyle and overeating high-fat, energy-dense foods. The United States is the most obese country in the Americas and the worlds 10th fattest, with 36.2% of its population having a BMI of over 30. Lack of physical exercise is a major contributing factor to the countrys obesity epidemic. High caloric intake is also linked to a high obesity rate.
10 Least Obese Countries
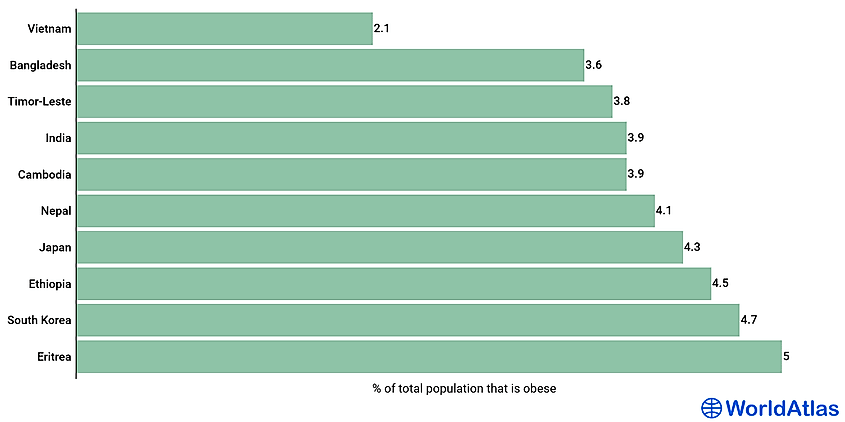
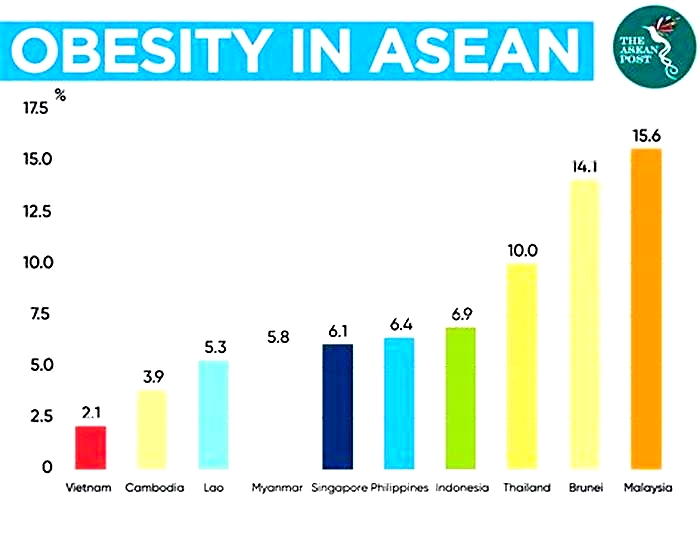
Vietnam is the least obese country, with only 2.1% of the adult population suffering from obesity. The countrys low ranking is a result of a combination of socioeconomic and cultural factors. Vietnamese mainly feed on local cuisine, which is mostly organic, with a lower level of oil. However, economic factors, such as long working hours and malnutrition, also contribute to the low ranking.
Bangladesh is the second-skinniest country, with obesity affecting only 3.6% of its adult population. However, the prevalence of obesity in the country is much higher in women than men. It is also one of the countries struggling with underweight and obesity, especially among adolescent children. Like Vietnamese, the Bangladeshi population depends on local cuisine, which is much healthier than imported, processed food. The population, especially men, are also more active.
3.8% of East Timors adult population are suffering from obesity, making it the third-least obese country. The country has a serious food deficit, with 27% of its residents suffering from food deprivation. Therefore, East Timors lower-ranking results from lack of access to food and not better-eating habits.
India, the worlds second-most populous country, has one of the lowest obesity rates, with only 3.9% of its adult population suffering from obesity. Most parts of the country are recovering from malnutrition and lack of access to food. Also, genetic factors are responsible for the countrys skinniness. However, India is slowly becoming more obese due to the rising middle class and unhealthy eating habits.
Cambodia, Nepal, Japan, and South Korea are the other four Asian countries on the list of ten least obese countries. In Cambodia, 3.9% of the adults are obese, while the proportions in Nepal and Japan are 4.1% and 4.3% respectively. In South Korea, 4.7% of the adult population is obese. About 80 of Cambodias population live in rural areas, where agriculture is the main economic activity. Therefore, the majority depend on food from the farm, which is much healthier than processed, high-sugar food. In Nepal, the lower ranking result from challenges in accessing food, especially for those living in remote areas.
Japanese are some of the world's healthiest people. An average adult consumes about 200 fewer calories than an American. Their traditional food also features less meat, more fish, and plenty of vegetables. They are also more active, which helps them in reducing the risk of becoming obese. South Korea also practices healthy eating habits, with its diet receiving considerable attention. Besides diet, Koreans have also invested in proper health education and supports local government in their obesity programs. The government also ensures that school diets and nutritious and healthy.
Ethiopia and Eritrea are the least obese countries in Africa. Only about 4.5% of adult Ethiopians are suffering from obesity, making it the worlds 8th least obese country. In Eritrea, only 5% of the adult population are obese. Eritrea and Ethiopia are some of the countries in Africa struggling with malnutrition and underweight. Undernutrition remains prevalent, especially in rural areas, where the majority live, due to the burden of famine.
Measuring Obesity

BMI is the most common matrix for assessing obesity in adults. It is also used to classify individuals as overweight or underweight. BMI is calculated by diving an individuals weight (kg) by the square of his height. For instance, a person weighing 65 kilos and is 1.5 meters tall will have a BMI of 28.9, meaning they are overweight but not obese.
An individual with a BMI of over 30 is considered obese. Therefore, 51 countries are considered either overweight or obese because they have a BMI of at least 25. Of the 51 countries, 22 are obese. 75 countries are underweight (BMI less than 18.5), while 64 countries are considered healthy, with a BMI range of 18.5 to 24.9.
Rank | Country | % of population that is obese |
|---|---|---|
1 | Nauru | 61 |
2 | Palau | 55.3 |
3 | Marshall Islands | 52.9 |
4 | Tuvalu | 51.6 |
5 | Tonga | 48.2 |
6 | Samoa | 47.3 |
7 | Kiribati | 46 |
8 | Federated States Of Micronesia | 45.8 |
9 | Kuwait | 37.9 |
10 | United States | 36.2 |
11 | Jordan | 35.5 |
12 | Saudi Arabia | 35.4 |
13 | Qatar | 35.1 |
14 | Libya | 32.5 |
15 | Turkey | 32.1 |
16 | Egypt | 32 |
17 | Lebanon | 32 |
18 | United Arab Emirates | 31.7 |
19 | The Bahamas | 31.6 |
20 | New Zealand | 30.8 |
21 | Iraq | 30.4 |
22 | Fiji | 30.2 |
23 | Bahrain | 29.8 |
24 | Canada | 29.4 |
25 | Australia | 29 |
26 | Malta | 28.9 |
27 | Mexico | 28.9 |
28 | Argentina | 28.3 |
29 | South Africa | 28.3 |
30 | Chile | 28 |
31 | Dominica | 27.9 |
32 | Uruguay | 27.9 |
33 | Syria | 27.8 |
34 | United Kingdom | 27.8 |
35 | Dominican Republic | 27.6 |
36 | Algeria | 27.4 |
37 | Oman | 27 |
38 | Tunisia | 26.9 |
39 | Hungary | 26.4 |
40 | Suriname | 26.4 |
41 | Lithuania | 26.3 |
42 | Israel | 26.1 |
43 | Morocco | 26.1 |
44 | Czechia | 26 |
45 | Iran | 25.8 |
46 | Costa Rica | 25.7 |
47 | Andorra | 25.6 |
48 | Venezuela | 25.6 |
49 | Ireland | 25.3 |
50 | Vanuatu | 25.2 |
51 | Bulgaria | 25 |
52 | Greece | 24.9 |
53 | Jamaica | 24.7 |
54 | Cuba | 24.6 |
55 | El Salvador | 24.6 |
56 | Belarus | 24.5 |
57 | Croatia | 24.4 |
58 | Belize | 24.1 |
59 | Ukraine | 24.1 |
60 | Spain | 23.8 |
61 | Nicaragua | 23.7 |
62 | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | 23.7 |
63 | Latvia | 23.6 |
64 | Montenegro | 23.3 |
65 | Barbados | 23.1 |
66 | Norway | 23.1 |
67 | Poland | 23.1 |
68 | Russia | 23.1 |
69 | Saint Kitts and Nevis | 22.9 |
70 | Haiti | 22.7 |
71 | Panama | 22.7 |
72 | Luxembourg | 22.6 |
73 | Romania | 22.5 |
74 | Solomon Islands | 22.5 |
75 | Colombia | 22.3 |
76 | Germany | 22.3 |
78 | Finland | 22.2 |
79 | Belgium | 22.1 |
80 | Brazil | 22.1 |
81 | Iceland | 21.9 |
82 | Cyprus | 21.8 |
83 | Albania | 21.7 |
84 | Georgia | 21.7 |
85 | France | 21.6 |
86 | Serbia | 21.5 |
87 | Honduras | 21.4 |
88 | Grenada | 21.3 |
89 | Papua New Guinea | 21.3 |
90 | Estonia | 21.2 |
91 | Guatemala | 21.2 |
92 | Kazakhstan | 21 |
93 | Portugal | 20.8 |
94 | Mongolia | 20.6 |
95 | Sweden | 20.6 |
96 | Slovakia | 20.5 |
97 | Netherlands | 20.4 |
98 | Paraguay | 20.3 |
99 | Armenia | 20.2 |
100 | Bolivia | 20.2 |
101 | Guyana | 20.2 |
102 | Slovenia | 20.2 |
103 | Austria | 20.1 |
104 | Azerbaijan | 19.9 |
105 | Ecuador | 19.9 |
106 | Italy | 19.9 |
107 | Denmark | 19.7 |
108 | Peru | 19.7 |
109 | Saint Lucia | 19.7 |
110 | Switzerland | 19.5 |
111 | Antigua and Barbuda | 18.9 |
112 | Botswana | 18.9 |
113 | Moldova | 18.9 |
114 | Trinidad and Tobago | 18.6 |
115 | Turkmenistan | 18.6 |
116 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | 17.9 |
117 | Namibia | 17.2 |
118 | Yemen | 17.1 |
119 | Kyrgyzstan | 16.6 |
120 | Lesotho | 16.6 |
121 | Uzbekistan | 16.6 |
122 | Eswatini | 16.5 |
123 | Malaysia | 15.6 |
124 | Zimbabwe | 15.5 |
125 | Gabon | 15 |
126 | Tajikistan | 14.2 |
127 | Brunei | 14.1 |
128 | Seychelles | 14 |
129 | Djibouti | 13.5 |
130 | Mauritania | 12.7 |
131 | Sao Tome and Principe | 12.4 |
132 | Cabo Verde | 11.8 |
133 | Cameroon | 11.4 |
134 | Ghana | 10.9 |
135 | Mauritius | 10.8 |
136 | Cote d'Ivoire | 10.3 |
137 | Gambia, The | 10.3 |
138 | Thailand | 10 |
139 | Liberia | 9.9 |
140 | Benin | 9.6 |
141 | Republic Of The Congo | 9.6 |
142 | Guinea-Bissau | 9.5 |
143 | Nigeria | 8.9 |
144 | Senegal | 8.8 |
145 | Sierra Leone | 8.7 |
146 | Maldives | 8.6 |
147 | Mali | 8.6 |
148 | Pakistan | 8.6 |
149 | Tanzania | 8.4 |
150 | Togo | 8.4 |
151 | Somalia | 8.3 |
152 | Angola | 8.2 |
153 | Zambia | 8.1 |
154 | Equatorial Guinea | 8 |
155 | Comoros | 7.8 |
156 | Guinea | 7.7 |
157 | Central African Republic | 7.5 |
158 | Mozambique | 7.2 |
159 | Kenya | 7.1 |
160 | Indonesia | 6.9 |
161 | North Korea | 6.8 |
162 | Democratic Republic Of The Congo | 6.7 |
163 | South Sudan | 6.6 |
164 | Sudan | 6.6 |
165 | Bhutan | 6.4 |
166 | Philippines | 6.4 |
167 | China | 6.2 |
168 | Chad | 6.1 |
169 | Singapore | 6.1 |
170 | Burma | 5.8 |
171 | Malawi | 5.8 |
172 | Rwanda | 5.8 |
173 | Burkina Faso | 5.6 |
174 | Afghanistan | 5.5 |
175 | Niger | 5.5 |
176 | Burundi | 5.4 |
177 | Laos | 5.3 |
178 | Madagascar | 5.3 |
179 | Uganda | 5.3 |
180 | Sri Lanka | 5.2 |
181 | Eritrea | 5 |
182 | South Korea | 4.7 |
183 | Ethiopia | 4.5 |
184 | Japan | 4.3 |
185 | Nepal | 4.1 |
186 | Cambodia | 3.9 |
187 | India | 3.9 |
188 | Timor-Leste | 3.8 |
189 | Bangladesh | 3.6 |
190 | Vietnam | 2.1 |
191 | Palestine | Data not available |
192 | Liechtenstein | Data not available |
193 | Monaco | Data not available |
194 | San Marino | Data not available |
195 | Vatican City | Data not available |
Table: Countries By Obesity. Source: CIA World Factbook