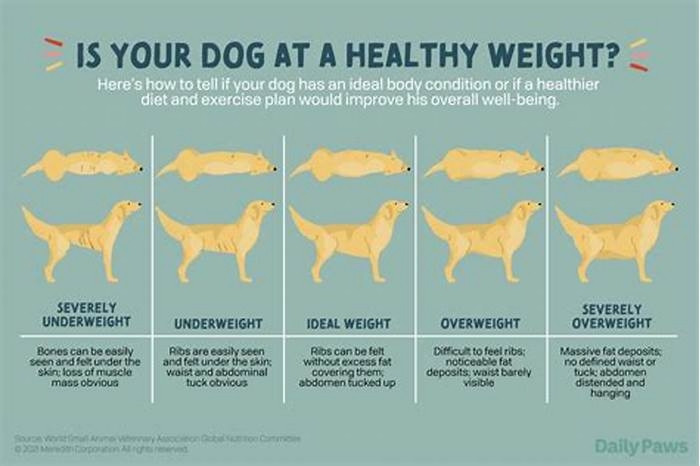
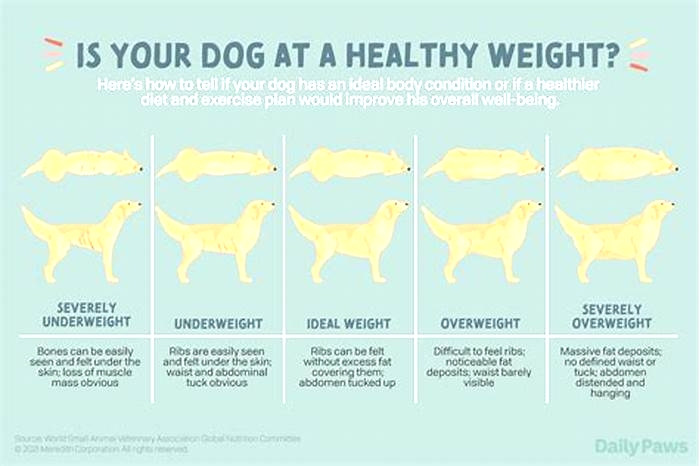
Can you be skinny but obese

Can You be Skinny and Obese?
Oh Yeah! There is a condition called Metabolically Obese Normal Weight (MONW). It is synonymous with Thin on the Outside and Fat on the Inside. Also known as TOFI.
How can being skinny and obese happen?
There are different kinds of fat. The subcutaneous type is the one under the skin and can get thick and manifest as obesity. The subcutaneous fat is known to be metabolically stable. Meaning it does not produce substances that can cause inflammation to the whole body.
Fat inside the abdomen is called visceral fat. The visceral fatis located in two areas. The first is in the omentum. The omentum is like an apron that hangs from the stomach and the transverse colon. If the omentum starts to accumulate fat, then it gets thick. That is what bulges out in beer bellies or soda pop bellies. The subcutaneous fat also adds to the bulge in that situation. The accumulation of omental fat is harmful because it can secrete toxic substances called pro-inflammatory cytokines that cause chronic illnesses like atherosclerosis and cancer.

The bigger problem is when fat accumulates in the liver, called the fatty liver. Three things can cause fatty liver. When there is a constant supply of high blood glucose, and the liver is filled up with glycogen, the liver will try to maintain a healthy blood sugar such that it sacrifices itself and changes the glucose into fat which is a denser form of energy and it stores it in the liver.
The second is fructose overload. Fructose comes from table sugar, which is sucrose. Sucrose is 50% glucose and 50% fructose. High-Fructose Corn Syrup or HFCS contains more fructose from 55 to 65%. It is in pop, bread, catsup, sauces, and most the processed foods.
The third is alcohol, which is metabolized, just like fructose in the liver. There is a big difference between fructose and glucose metabolism.
The Difference between Glucose and Fructose Metabolism
After ingesting glucose, 80% is used by the body for normal body function. Only 20% of glucose goes into the liver to make glycogen. In contrast, 100% of the fructose goes to the liver. While the liver can metabolize part of the fructose into glucose, if sugar and HFCS consumption is high, then the liver becomes fully loaded right away with glycogen. Fatty infiltration of the liver leads to insulin resistance and then high blood sugar.
How Fat Inside the Abdomen Develops
If the high sugar, starch, and HFCS consumption continue, glucose becomes fat and spreads in the blood as VLDL or triglycerides. The fat cells then get deposited in the other organs in the abdomen, including the pancreas, leading to diabetes. The thickened omentum later secretes inflammatory substances. A sedentary lifestyle is a significant risk factor in the development of the fatty liver.
Fatty liver and hyperinsulinemia are the cornerstones of metabolic syndrome.

The At-Risk Obese and Metabolically Healthy Obese
This classification applies to a person who has a high BMI (>25), high visceral fat content, high-fat mass, high blood sugar, low insulin sensitivity, high triglycerides, and low HDL. 80% of people with high BMI have this.
There is also a Metabolically Healthy Obese (MHO). They have a high BMI and high-fat mass, but normal to a high level of insulin sensitivity, low triglycerides, healthy blood sugar, and high HDL. They account for 20% of the obese population.
Summary:
Being a TOFI can also lead to insulin resistance, high blood sugar, diabetes, abnormal lipid profile, atherosclerosis, heart disease, and cancer. Just because you have an average weight does not always mean you are healthy. TOFI can also be seen in children.
Related Readings:
- How Will You Know if You are TOFI?
- Can You be Skinny and Obese?
- What Does Waist Circumference Really Measure?
- Why Do Bellies Bloat?
Photo Credits: Wikipedia. Public Domain
2019 DrJesseSantiano.com All Rights Reserved
MEDICAL DISCLAIMER
People With Obesity Have Slim Chance of Obtaining Normal Body Weight
Researchers say less than 1 percent of people with obesity get back to a healthy body weight. Experts say new approaches are needed to fight this common ailment.
For every 100 people who have obesity, only perhaps one will reach a healthy weight again, a new study states.
Since obesity is directly linked to a higher incidence of disease and a shorter lifespan, thats a big problem.
Researchers with the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) in the United Kingdom used a decades worth of digital health records for 278,982 people 129,194 men and 149,788 women and concluded current methods of getting people to lose weight arent working.
The study, published Thursday in the American Journal of Public Health, highlights the real world outcomes for adults with obesity in developed countries.
In the United States, almost 35 percent of adults and 17 percent of children or more than 91 million people have obesity, according to
Obesity is defined as when a persons body mass index, or BMI, is greater than 30.
Researchers used only data from patients with at least three BMI measurements between 2004 and 2014. They found the odds of losing weight directly correlated with how much weight a person carried.
Read More: Better Late Than Never, Doctors Begin to Treat Obesity
Researchers said the overall chances of a man with obesity obtaining a normal body weight were 1 in 210. For women, it was 1 in 124.
Those odds worsen as a persons weight increases.
Men with a BMI over 40 had a 1 in 1,290 chance of becoming healthy while women in that category had a 1 in 677 chance.
Losing 5 percent of their weight was successful for about 10 percent of women and 1 in 12 men.
Once an adult becomes obese, it is very unlikely that they will return to a healthy body weight, Alison Fildes, Ph.D., first author of the study from the Division of Health and Social Care Research at Kings College London, said in a press release.
Keeping the weight off is an even more difficult battle.
About 53 percent of patients regained lost weight within two years and 78 percent put the weight back on within five years.
A third of all patients had fluctuating weight, signifying many battles were lost and won before any kind of victory could be achieved.
Losing 5 to 10 percent of your body weight has been shown to have meaningful health benefits and is often recommended as a weight loss target, said Fildes. These findings highlight how difficult it is for people with obesity to achieve and maintain even small amounts of weight loss.
Earlier this year, researchers published
Experts: Obesity Is Biologically Stamped In, Diet and Exercise Wont Cure It
The NIHR study concludes that current obesity treatments are failing to achieve sustained weight loss for the majority of patients with obesity.
When analyzing patients, the NIHR specifically excluded patients who underwent bariatric bypass surgery, an invasive method thats shown to help in patients with severe obesity.
Martin Gulliford, the NIHR studys senior author and professor of health and social care research at Kings College London, says the data shows diet and exercise alone arent getting the needed results.
Current strategies to tackle obesity, which mainly focus on cutting calories and boosting physical activity, are failing to help the majority of obese patients to shed weight and maintain that weight loss, he said. The greatest opportunity for stemming the current obesity epidemic is in wider-reaching public health policies to prevent obesity in the population.
Read More: Artificial Light Associated with Obesity
What Does Skinny Fat Mean?
Skinny fat is a term that refers to having a high percentage of body fat and a low amount of muscle.
Its a common misconception that small or thin bodies are an indicator of good health. However, those with higher body fat and lower muscle mass even if they have a body mass index (BMI) that falls within a normal range may be at risk of developing the following conditions:
Read on to learn what the term skinny fat means and what lifestyle habits may contribute.
Skinny fat doesnt have a standardized definition and isnt a medical term, so different people use the term in various ways.
Its usually used to refer to less muscle tone and strength as well as a relatively high body fat percentage, despite having a normal BMI. This term is often used negatively to describe somebody who isnt physically fit.
Somebody who is considered skinny fat may have a large amount of visceral fat and may not have much muscle definition.
Everyones body is different. Some people are more genetically predisposed to have a higher body fat percentage and less muscle than others.
Other factors like exercise and nutrition habits, age, and hormone levels can also contribute to body size.
Exercise and dietary habits
When you exercise, your body releases anabolic hormones that stimulate muscle building. Exercise also
Exercising regularly can help you avoid hormonal changes that negatively impact your body composition and make you more prone to storing fat.
Eating a diet high in refined sugar can also negatively impact your body composition. A
Sex
Anyone can be considered skinny fat. Since the term is subjective, its hard to measure whether its more common in certain sexes.
Age
Older adults may be at the highest risk of muscle loss and an increase in body fat, due to hormonal changes that make it more difficult to maintain muscle.
Age-related muscle loss is called sarcopenia, which is often accompanied by an increase in body fat.
Hormone imbalances
Hormonal imbalances may contribute to increased body fat and changes in body fat storage.
For example,
A person who doesnt exercise frequently or maintains an unbalanced diet may be at an elevated risk of conditions such as
The medical term for someone whos lean but has a metabolic profile that puts them at risk of developing metabolic disease is a metabolically obese, normal weight individual.
The five major risk factors for this condition are:
Metabolically obese, normal weight individuals over age 65 are at an elevated risk of
Research has also found that having a high mass of fat and a combination of low muscle mass and strength may be associated with cognitive decline.
When you eat food high in sugar, your blood sugar rises and your body produces insulin to shuttle the sugar into fat and muscle cells for storage.
Chronically elevated insulin levels can lead to insulin resistance, which happens when your body stops responding to insulin. Insulin resistance is linked to increased body fat, especially
Your body needs protein and many other nutrients to efficiently build muscle tissue. Not getting enough essential nutrients in your diet can impair your bodys ability to build muscle.
Recommended dietary measures
Here are some dietary measures that can improve your body composition:
- Minimize simple carbohydrates and focus on getting most of your carbohydrates from whole grains, fruit, and vegetables.
- Include plenty of protein in your diet.
- Minimize sugary or high-calorie beverages like sodas, alcohol, and juices.
- Minimize your consumption of added sugars.
- Minimize your intake of ultra processed foods like pastries, sweetened breakfast cereal, and candy bars.
- Eat high-protein foods after you exercise.
Your lifestyle habits play a big role in determining your body composition and your overall health.
Along with diet and exercise habits, poor sleep and too much stress can also contribute to increased body fat.
Here are some dos and donts that might help improve your body composition.
Increasing the amount you exercise may help you improve your body composition.
Despite what some websites claim, theres no specific workout or exercise that is known to reduce skinny fat body composition. Instead, look for a type of exercise you enjoy and make it a part of your weekly routine.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recommends the following:
- Get at least
150 to 300 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week. - Do strength training for all major muscles at least twice per week.
Skinny fat is a term that refers to having a relatively high percentage of body fat and a low amount of muscle mass, despite having a normal BMI.
People of this body composition may be at a heightened risk of developing diabetes and heart disease.
If its not already part of your routine, exercising regularly and eating a balanced and nutrient-dense diet can help improve or maintain your body composition.