At what age are Labradors mature

When Do Labradors Mature? (2024)

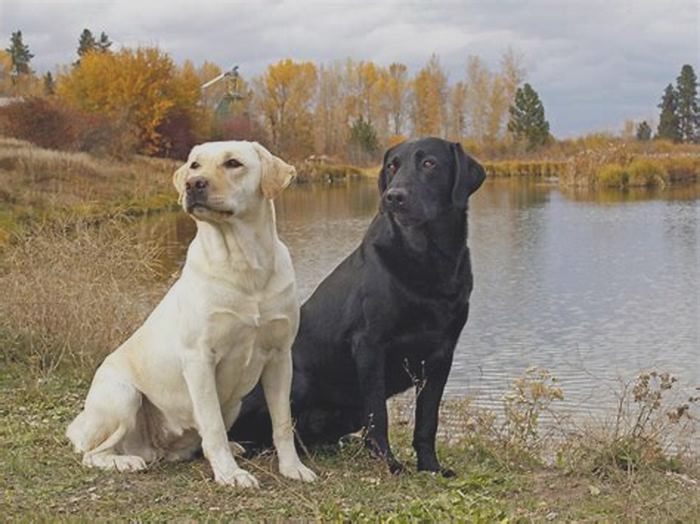
There must be a good reason that Labradors have firmly held onto the #1 position in popularity charts for nearly 30 years, right?
In terms of friendliness, affection, intelligence, and loyalty, this breed is hard to beat. A non-aggressive nature, a playful and exuberant disposition, an eager-to-please attitude, and a love of people has endeared the Labrador to thousands of dedicated enthusiasts.
What you may not be aware of is that while Labs are absolutely wonderful companions, it can take a while for them to reach that point. Actually, quite a while.
When do Labradors mature? Labs will reach physical maturity by 18 months. Sexual maturity will occur between months 6 -9. Though some maturity will be noted before age 2, a Lab will usually take 2 to 4 years to reach full mental maturity, and by the age of 5, a Lab should be well mannered, calm, and a joy to own.
It would be great to wake up one day and say, Today is my Labs first birthday! No more puppy issues! No more chewing slippers! Now hes an adult! Yippee! With a Lab, that line of thought is wishful thinking. Not going to happen.
Heres what you can expect as your Lab slowly inches his way to full maturity and becomes the dog of your dreams and your best friend.
Stages of Labrador Maturity
Becoming an adult doesnt happen overnight. Your Lab will go through several developmental phases, some more drawn out than others, before becoming fully mature.
Still, maturity in Labs can be difficult to measure, because, in some ways, a part of them always seems to retain some endearing puppy characteristics. Really, thats one of the main reasons they are universally adored.
Lets look at the three main maturity milestones your Labrador will reach (eventually).
Physical Maturity
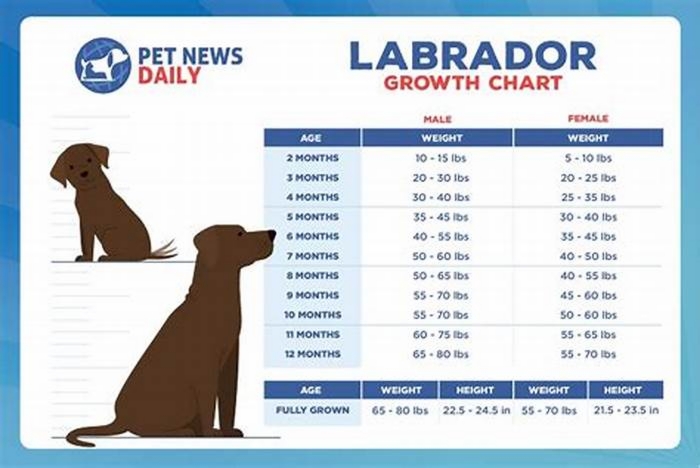
Most Labs will be close to their final height by around the 9-month mark. By 12 months of age, a Lab has reached his full height. However, theyre not quite done growing yet. Until about 18 months, a Lab will continue to add muscle and fat to his frame and fill out quite a bit, leaving behind that gangly, adolescent look.
How Big Will Your Labrador Get?
According to the American Kennel Club, an adult male Labrador should reach 22 24 inches tall at the withers (highest point of the shoulders) and weigh between 65 and 80 pounds. Females are typically smaller and should stand between 21 to 23 inches tall and weigh 55 70 pounds.
Is There a Difference in Size Between English Labs and American Labs?
English Labradors and American Labradors arent separate breeds, just different types of Labrador Retrievers. Generally, English Labs have a stockier appearance, a broader head with a shorter muzzle, a thicker coat, and are slightly more laid-back than their American counterparts. Theyre usually an inch or two shorter but often weigh more than American types.
American Labs have a finer bone structure, more slender appearance, and narrower, longer muzzles. Theyre usually more athletic and energetic and are typically taller and lighter than the English type.
Fun fact: English Labs are more commonly seen in the show ring while American Labs are used more extensively in field trials due to their athleticism and above-average enthusiasm, but both types are Labradors through and through.
Sexual Maturity
Anytime between the ages of 6 -9 months both male and female dogs become sexually mature, capable of producing a litter. Labradors tend to hit sexual maturity a bit later than other breeds of comparable size, but by the time they reach 9 months of age, theyre usually fully capable of reproducing.
Be sure to speak with your veterinarian about having your Lab spayed or neutered. While sterilization was once commonly encouraged before the onset of puberty, recent findings have shown that postponing altering until after a dogs first birthday may be a better option as his body benefits from the natural hormone production associated with sexual maturity.
Mental Maturity
This stage of a Labradors maturity is often thought of as somewhat elusive, but when it eventually does occur, the difference is like night and day. Large breeds like Labs take longer to mature physically, sexually, and mentally, but Labs, in particular, are famous for taking an extra-long time to finally grow up and calm down a little.
Brace yourself, because the answer here may be far from what you were expecting. Labs retain a puppy-like temperament for at least two full years, but for many Labs, signs of complete maturity wont be seen until theyre closer to their 4th birthday. Many Labs will still exhibit a puppys exuberance, energy, and enthusiasm for fun until they reach 5 years of age.
While defiance, limit testing, and destruction should be on a downward trend by the second year, a 2-year-old Lab is still very much a puppy and will have a ton of energy. Labs who are between 2 and 4 years of age usually have an unrivaled zest for life and are always ready for action.
The question is whether you will dictate your Labs activities or allow him to choose his own form of exercise and entertainment.
Be warned, you probably wont be thrilled with whatever your Lab comes up with. Chewing through Sheetrock, deciding its time to replace the kitchen floor, systematically removing your baseboards one by one these are all possibilities a Lab may come up with when left to his own devices.
For this reason, a sturdy crate is highly recommended until your Lab is fully mature and trustworthy enough to be left on his own in the house.
By the fifth year, most Labs will be well behaved, calm, obedient companions with lower energy levels and a true desire to please their owners.
Signs of Maturity
Of course, every Lab is different, and theres no magic age when a switch is flipped and they suddenly decide to be perfect pets. Most owners will, however, begin to notice some improvements during their Labs second year.
Destructive behavior will begin to subside, not everything will still be viewed as a game, less time will be spent roughhousing, and more time will be spent relaxing. Youll also notice that your maturing Lab has established a predictable routine as he goes about his days.
Puppy and adolescent behaviors such as stealing shoes, testing the limits, and outright defiance will be gradually replaced by a more calm demeanor and trustworthy behavior.
Will the Teething and Chewing Ever End?
Take heart! By the age of 8 months, your Labradors adult teeth should all be in, the needle-sharp puppy teeth will be a distant memory, and teething will be over. Does this mean that the endless chewing and mouthiness will magically disappear? Unfortunately, no.
Labradors, by nature, are a mouthy, orally fixated breed. They were, after all, bred to retrieve for hours on end, using their mouths to carry back downed waterfowl (and fish a long time ago) to their masters.
When playing outside, many Labs will constantly have something in their mouths such as a stick, pine cone, ball, anything will do really. Indoors, if appropriate toys (like a Kong) arent made available, a Lab will find something to chew on, often to the owners dismay. Socks, shoes, remotes, table legs, the list goes on and on (have you ever seen Marley and Me?).
Channeling that love of chewing into appropriate outlets is something youll need to do if youre to survive life with a Lab. A good variety of chew toys, the more indestructible the better, will definitely help.
Training your Lab what is acceptable and what is an absolute no-no is crucial. Whenever you find him mouthing something inappropriate, especially if that something happens to be a human hand, immediately say, No! in a firm voice, and replace the object with an appropriate toy.
With time and patience on your part, your Labrador will learn, but its up to you to teach him and provide him with lots of alternatives to satisfy his need to chew.
When Do Labradors Mature: A Comprehensive Guide

Labrador Retrievers, with their friendly nature and versatile abilities, have long held a cherished place in the hearts of dog lovers around the world. These lovable canines are renowned for their intelligence, loyalty, and gentle temperament.
As one of the most popular dog breeds globally, Labradors have enriched countless households and played significant roles as service dogs, therapy dogs, search and rescue dogs, and much more. Truly understanding the maturation process of Labradors is crucial for every owner or prospective owner to ensure their well-being throughout their development.
Importance of Understanding the Maturity Process in Labradors
Gaining a comprehensive understanding of Labrador maturation is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it enables owners to provide appropriate care during each stage of a Labradors life cycle.
Puppies require different nutrition levels than fully grown adults, and their exercise needs change as they mature. By comprehending the specific developmental milestones, owners can ensure proper physical and mental stimulation, preventing potential health issues or behavioral problems.
Understanding the maturity process aids in setting realistic expectations for training and behavior. Labradors, like any other breed, exhibit distinct behaviors at different stages of development.
Recognizing these patterns allows owners to tailor their training methods accordingly and effectively address any challenges that may arise. Comprehending Labrador maturation instills a deeper bond between humans and their furry companions.
Appreciating the changes a Labrador undergoes as it matures fosters empathy and patience toward their unique needs. It enables owners to appreciate each phase of development with a sense of wonder while providing a nurturing environment that promotes growth and well-being.
A general timeline of Labrador maturation

Puppyhood (0-6 months)
During the first six months of a Labradors life, they undergo rapid growth and development. Puppies are curious, energetic bundles of joy, always exploring their surroundings with boundless enthusiasm.
Their physical growth is particularly noticeable during this stage, as they gain weight and increase in size week by week. It is important to note that Labradors have a tendency to grow quickly, so proper nutrition and regular veterinary check-ups are essential to ensure their healthy development.
This phase is marked by the teething and chewing stage. As their baby teeth fall out and adult teeth come in, Labradors may experience discomfort and an intense desire to chew on anything they can find as a means of relieving the discomfort.
Providing appropriate chew toys can help redirect their chewing behavior toward acceptable outlets. Alongside physical milestones, puppyhood is also an ideal time to introduce basic obedience training using positive reinforcement techniques such as rewarding good behavior with treats or praise.
Adolescence (6-12 months)
As Labradors enter adolescence between six to twelve months old, their physical growth slows down compared to the previous puppyhood stage. Their energy levels surge, making them even more active and curious than before.
It is crucial for owners to provide ample exercise opportunities during this period to meet their growing needs for mental stimulation and physical exertionotherwise, Labradors may exhibit behavioral issues like excessive chewing or digging due to pent-up energy. Advanced obedience training becomes increasingly important at this stage as well.
Teaching commands such as sit-stay or recall helps reinforce good manners while ensuring safety in various situations outside the home environment. Socialization should be prioritized during adolescenceexposing Labradors to different environments, people, and animals will help them develop confidence and become well-adjusted adult dogs.
Young adulthood (1-2 years)
As Labradors reach young adulthood, usually between one to two years old, they attain physical maturity. Their growth plates close, and their skeletal structure becomes fully developed. It is essential to remember that mental maturity may still be a work in progress during this phase.
Young adult Labradors often display bursts of energy and playfulness but can also exhibit moments of immaturity or impulsivity. It is important to continue providing consistent training and guidance to refine their behavior further.
Another notable aspect of young adulthood in Labradors is the emergence of their full adult coat. The shiny and dense coat that we associate with Labradors gradually grows during this stage, requiring regular grooming to maintain its health and appearance.
Factors Affecting Labrador Maturation Rate

Environmental Factors
Labrador maturation rate can be influenced by various environmental factors that contribute to their overall growth and development. One crucial aspect is nutrition, as providing a proper diet is essential for optimal growth.
Puppies require a diet rich in high-quality protein, necessary vitamins, and minerals to support their bone development and muscle growth. Similarly, adequate exercise plays a vital role in Labradors maturation.
Regular physical activity helps develop strong muscles, improves cardiovascular health, and contributes to overall physical fitness. Engaging Labradors in activities such as walking, running, swimming, or playing fetch not only promotes muscle development but also aids in maintaining a healthy weight.
ental stimulation through interactive play and training is crucial for their cognitive development. Engaging Labradors with puzzle toys, obedience training sessions, or interactive games enhances their problem-solving skills and mental agility.
Genetics
The genetics of Labradors also plays a significant role in determining their maturation rate. Within the Labrador breed itself, variations can exist due to different lines of breeding over the years. Some lines may mature earlier or later than others due to specific genetic traits passed down through generations.
Parental traits strongly influence the maturation rate of individual puppies within a litter. Certain inherited traits may influence how quickly Labradors reach physical maturity or how fast they develop.
Health Considerations
Health conditions can have an impact on the maturation rate of Labradors as well. Any underlying medical issues can potentially affect their growth process and overall maturity timeline. For instance, certain health issues such as hip dysplasia or joint problems may lead to slower physical development or delayed skeletal maturity in Labradors.
It is important for dog owners to monitor any potential health concerns closely and consult with veterinarians to ensure proper management and treatment are provided. By addressing health conditions promptly, Labradors can have the best chance for a healthy and timely maturation path.
Special considerations for different aspects of Labradors maturation

Physical maturity
Labrador Retrievers undergo specific changes as they physically mature. One crucial aspect is the closure of growth plates, which are responsible for the lengthening of bones during development.
This process typically occurs between 10 and 18 months of age in Labradors. It is important to monitor their growth plates closure to ensure proper skeletal development and prevent potential orthopedic issues.
uscle tone development plays a vital role in physical maturity. Regular exercise, such as daily walks or playtime, helps build strong muscles and maintains overall physical health.
Mental maturity
Mental maturity in Labradors is just as significant as their physical growth. Socialization plays a pivotal role in their mental development. Introducing them to various environments, people, animals, and situations from an early age helps them become well-rounded adults with balanced temperaments.
Positive interactions during socialization can shape their behavior positively and enhance their ability to adapt to new experiences throughout life.
Maturation Process of Male and Female Labradors
Understanding the maturation process of Labradors is crucial for any owner, especially when considering breeding or simply understanding the growth phases of their furry companion. Lets delve into the distinct differences between male and female Labradors in terms of sexual maturity and physical development.
Male Labradors
Sexual Maturity: Male Labradors typically reach sexual maturity between 6 and 9 months of age. This means they can become fertile and capable of breeding quite early. Full sexual maturity, where they are most potent for breeding, is usually achieved a few months later.
Physical Maturity: While their sexual development might seem rapid, their physical growth takes a bit more time. Labradors, in general, attain their full physical maturity a while after their first birthday. This is when they reach their optimal size and weight.
Female Labradors
Sexual Maturity: Female Labradors have a slightly different timeline. They usually reach sexual maturity around 2 years of age, though some might experience it earlier. Labradors first heat cycle can be observed as early as 6 months of age and tends to reoccur approximately every 6 months throughout their life. For breeding purposes, its often recommended to wait until they are around 2 years old.
Physical Maturity: Just like their male counterparts, female Labradors typically reach their full physical maturity a while after their first birthday.
Neutering and Its Impact on Labrador Maturation

Neutering, a common practice among dog owners, can have specific implications on the maturation rate of Labradors. Lets delve deeper into the potential effects and what research has to say about this procedure.
Delayed Closure of Growth Plates
One of the most significant impacts of neutering Labradors, especially when done before puberty, is on their joint growth. Neutering large breed dogs before they reach puberty can lead to the growth plates not closing as they should. This is particularly concerning when neutering is done before the age of 6 months, as it has been associated with a significant increase in the rate of joint disorders in Labrador retrievers.
Increased Risk of Joint Disorders
The age at which a Labrador is neutered can play a pivotal role in their joint health. Neutering Labradors at a young age, especially before they turn 6 months old, has been linked to a higher likelihood of joint disorders. Conditions like hip dysplasia become more prevalent. In fact, research indicates that neutering at less than 6 months old can double the chances of one or more joint disorders manifesting.
Impact on Cancer Occurrence
The relationship between neutering and the occurrence of cancer in Labradors is a bit more complex. Some studies suggest that neutering has minimal to no effect on the emergence of specific cancers in Labrador retrievers. Other research indicates that neutering, regardless of the age at which its done, can increase the incidence of certain cancers, such as lymphosarcoma (LSA), in the breed.
Conclusion
Understanding When Do Labradors Mature is crucial for every Labrador owner. Labradors, with their playful nature and boundless energy, can sometimes be mistaken as perpetual puppies. This can lead to misconceptions about their growth and development. Recognizing the distinct phases of their maturation, from physical growth to behavioral changes, helps in providing them with the right care and training.
If youre a proud Labrador parent, wed love to hear from you! Have insights or personal stories about your Labs maturation journey? Share your experiences in the comments below!